The intervention used in this research was based on the Internal Family Systems model that sees an individual’s personality as made up of different sub-personalities
本研究所采用的干预方法基于家庭内部系统模型,认为个体的人格由不同的子人格性组成。
As social creatures, accurately recognising and understanding the mental states of others (their intentions, knowledge, beliefs, etc.) is crucial to our social bonds and interactions. In fact, in today’s multi-cultural world and strongly divided political climate, this skill – known as Theory of Mind – is perhaps more important than ever. A recent study published in the Journal of Cognitive Enhancement proposes that an effective way to develop our Theory of Mind lies in learning to better understand ourselves.
作为社会生物,准确认识和理解他人的心智状态(他们的意图、知识、信念等)对我们的社会关系和相互作用至关重要。事实上,在当今多元文化的世界和极度分裂的政治氛围中,这种被称为心理理论的技能也许比以往任何时候都更重要。最近发表在《认知提高》杂志上的一项研究表明,发展我们的心理理论的有效方法在于学习更好地了解自己。
Anne Böckler and colleagues, based at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, recruited 141 participants to take part in a three-month long contemplative training course that teaches people to take the perspective of the different aspects of their own personalities.
Anne Böckler和她的同事,在莱比锡的人类认知与脑科学马克斯-普朗克研究,招募了141名被试参加了为期3个月的长程冥想训练课程,教导人们了解自己性格的不同 的方面。
Before they started, the participants completed a test of their Theory of Mind: they watched short video clips of people describing autobiographical events, then answered a questionnaire about the storyteller’s intentions, thoughts and goals.
在他们开始之前,参与者完成了他们的心理理论的测试:他们观看了描述自传事件的短片,然后回答了一个关于说书人意图、想法和目标的问卷。
Next, the participants were taught to identify and label six ‘inner parts’ or sub-personalities within themselves, for example ‘the caring part’, ‘the inner happy child’, ‘the vulnerable part’. They could modify or add to this list at any time during the training course.
接下来,参与者被教导要识别和标注他们自己的六个“内在的部分”或“子人格”,例如“关心的部分”、“内在的快乐小孩”、“易受伤害的部分”。他们可以在培训期间随时修改或添加 这个表格。
The course itself consisted of two key components that the participants practised daily for thirty minutes, and at a two-hour guided weekly training sessions. The first component was an ‘observing-thoughts’ meditation, in which participants observed their thoughts objectively, de-identified from them (i.e. observed them in a detached way), then classified the thoughts into categories of me/other, past/future or positive/negative. The second component was a perspective-taking exercise which participants conducted in pairs, alternating between the role of speaker and listener. The speaker recounted an event from their day from the perspective of one of their randomly selected inner parts. Aware of the speaker’s various inner parts, the listener had to guess which one was talking.
课程本身由两个关键部分组成,参与者每天练习三十分钟,并在每周进行两小时指导训练。第一个部分是“观察-思维”的冥想, 参与者客观地观察了他们的想法,从他们自己之中确认自己(即以超然的方式观察他们),然后把这些想法分类为我/其他人,过去/未来或正/负。第二个组成部分是一个观点 采纳练习,即参与者轮流练习,在说话者和听者的角色之间交替进行。演讲者从他们的一个随机选择的内部部分叙述了一天中发生的一件事。听者意识到了说话者的各种内部因素,就不得不猜测是哪一 部分在讲话。
These perspective-taking exercises and the concept of ‘inner parts’ are based on the Internal Family Systems (IFS) model; an approach used in psychotherapy. The model sees an individual’s personality as made up of different sub-personalities, each with its own set of behaviours, cognitions and affects. The current study is part of a larger research project which draws from the model’s principles, successfully implemented in a therapeutic setting (such as with rheumatoid arthritis patients), and applies them to a non-clinical, healthy, adult population with the aim of improving mental well-being and social intelligence.
这些观点采纳练习和“内在部分”的概念是基于内部家庭系统(IFS)模型;心理治疗中使用的一种方法。该模型认为个体的人格由不同的子个性组成,每个个体都有自己的一套行为、认知 和情绪感受。目前的研究是一个较大研究项目的一部分,它从模型的原理中提出,在治疗环境中成功实施(如类风湿性关节炎患者),并将其应用于非临床、健康、成年人口以提高 心智幸福感和社会智力。
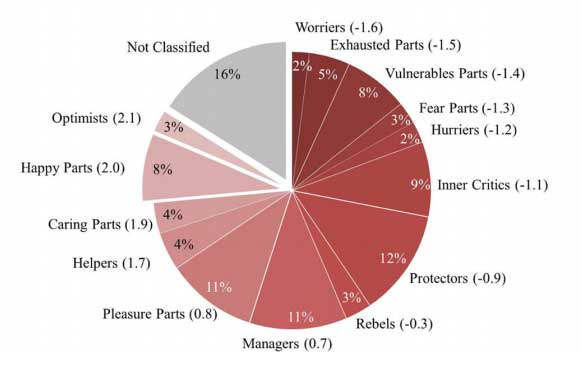
On average, the participants in the current study identified 11 inner parts to their personalities, of which 44 per cent were labelled by independent judges as negative traits and 56 per cent were positive traits. The researchers organised the participants’ different personality parts into related trait types according to the IFS model, the most common being: Protectors (12 per cent), Managers and Pleasure Parts (both 11 per cent), Inner Critics (9 per cent), and Vulnerable Parts (8 per cent).
平均而言,本次研究的参与者确定了他们性格的11个内部部分,其中44%个被独立的判断者评定为负面特质,56%个为积极特质。,研究者根据IFS模型将参与者的不同性格部分组织成相关的特质类型,最常见的是:保护者(12%)、管理者和快乐部分(11%个)、内 在批评者(9%)和易受攻击的部分(8%)。
After completing the training course the participants re-took the same Theory of Mind test that they’d taken at the start of the study. Improvement in Theory of Mind was correlated with the number of different inner personality parts identified – the more facets the participants were able to recognise within themselves, the better they seemed to become at understanding others. This is reflected in neuroimaging research, where the processes of perspective-taking of the self and others utilise shared neural mechanisms.
在完成培训课程后,参与者重新接受了他们在研究开始时所做的同样的心理理论测试。心理理论的改善与不同内在人格的认同有关——参与者识别他们自己的能力越强,他们在理解他人方面似乎就越好。这反映在神经影像研究中 ,即,利用共同神经机制采纳自己和他人观点的过程。
Interestingly, the correlation between number of parts of self identified and improvement in Theory of Mind was even stronger in those who identified more negative parts.The researchers propose thatthis supports the theory that people are naturally resistant to looking for negative aspects of their personality, therefore those who do are thought to be working more profoundly to better understand themselves. In addition to the result of a better understanding of the mental states of others, this deeper work also improves psychological wellbeing, as it is widely acknowledged in clinical psychology that accepting negative emotions is beneficial to mental health.
有趣的是, 心理理论中自我不同部分的认同和改善也出现了在那些认同更多负面部分的人中。研究人员认为,这一理论支持了人们寻找自己性格中消极方面的本能,因此,那样做的人可以更深刻地了解自己的工作。 这项研究除了能更好地了解他人的心理状态之外,这项更深层次的工作也改善了心理健康,正如临床心理学中普遍承认的那样,接受消极情绪有益于心理健康。
The purpose of identifying the different aspects of our personalities is to understand that through them one can view a single situation through a handful of different outlooks; we learn to see the self
认同我们人格中的不同方面的目的是要明白,通过他们,我们可以通过一系列不同的观点来看待一个单一的情况;我们学会了了解自己。
—Know Thy Selves: Learning to Understand Oneself Increases the Ability to Understand Others
https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2Fs41465-017-0023-6.pdf
www.psychspace.com心理学空间网